Subproject A04
Subproject A04
Microwave Interferometer for Cardiovascular and Respiratory Monitoring
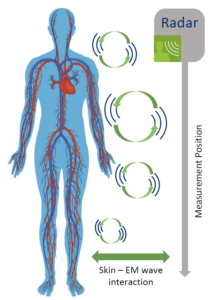
The A04 project is committed to measuring vital signs using radar technology. This involves studying microscopic movements on the body’s surface with radar and extracting vital signs such as heart rate and breathing using specialized algorithms. In project A04, we are focused on developing the necessary sensors and conducting fundamental research on the interaction of waves with the human body’s surface.
The development of these radar systems encompasses numerous subfields, including electronics, frontend design, and antenna construction. We employ systems operating at 61 GHz or 122 GHz frequencies, enabling us to measure microscopic movements precisely. Utilizing our „Emrad“ system within the Empkins project framework, we are compiling an extensive database of radar data. This database is pivotal for testing further advancements in machine learning and deep learning approaches.
This innovative methodology will allow for non-invasive, accurate, and reliable measurement of vital signs. Advanced radar technology and artificial intelligence synergy open up new medical monitoring and diagnostic possibilities.
Contacts
Prof. Dr. Alexander Kölpin
Principal Investigator
Nils Albrecht, M.Sc
Doctoral Candidate
Kristina Heß
Associtated Doctoral Candidate
Dominik Langer, M.Sc
Associated Doctoral Candidate
Hui Lu, M.Sc
Associated Doctoral Candidate
Marvin Wenzel, M.Sc
Associated Doctoral Candidate
Additional Information
- , , , , , , , :
EmRad: Ubiquitous Vital Sign Sensing using Compact Continuous-Wave Radars.
IEEE Open Journal of Engineering in Medicine and Biology (2024), S. 1-10. ISSN: 2644-1276. DOI: 10.1109/OJEMB.2024.3420241. - , , , , , , , , , , , , , , :
A Review and Tutorial on Machine Learning- Enabled Radar-Based Biomedical Monitoring.
IEEE Open Journal of Engineering in Medicine and Biology (2024), S. 1-22. ISSN: 2644-1276. DOI: 10.1109/OJEMB.2024.3397208 - , , , , :
Integration Approach for Radar Transceiver MMICs with Integrated Antennas Enabling Adaptability to Customized Passive Frontend Design.
IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium, IMS 2024 (Washington, 2024). DOI: 10.1109/IMS40175.2024.10600437 - Tegowski B., Koelpin A.:
Accuracy Limitations of Interferometric Radar Owing to the Radar Cross Section of Its Antenna.
IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques 72 (2024), S. 4317-4324. ISSN: 0018-9480. DOI: 10.1109/TMTT.2024.3350350 - , :
Nonlinear Distortion Effects of Vibration-Sensing Interferometric Radar Systems Due to Self-RCS.
25th International Microwave and Radar Conference (Wroclaw, 2024). DOI: 10.23919/MIKON60251.2024.10633969 - Tegowski B., Langer D., Wenzel M., Albrecht NC., Kölpin A.:
Near-Field Scattering Phenomena in Monostatic Radar Applications Derived From Physical Optics.
IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation (2024), S. 1-1. ISSN: 0018-926X. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2024.3486905 - , , :
Empirical Study on the Antenna-Dependent Accuracy of Continuous- Wave Radars.
15th German Microwave Conference (Duisburg, 2024). DOI: 10.23919/GeMiC59120.2024.10485343 - , , , , , :
Long-Distance Heart Sound Detection using 122 GHz CW Radar with 3D Printed High-Gain Antennas.
IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium, RWS 2023 (Las Vegas, 2023). DOI: 10.1109/RWS55624.2023.10046319 - , , , , :
Characterization of the Influence of Clothing and Other Materials on Human Vital Sign Sensing using mmWave Radar.
53rd European Microwave Conference, EuMC 2023 (Berlin, 2023). DOI: 10.23919/EuMC58039.2023.10290459 - , , , , , , , , , , :
Contactless Heart Rate Estimation using a 61 GHz Continuous-Wave Radar.
IEEE-EMBS International Conference on Body Sensor Networks: Sensor and Systems for Digital Health (MIT Media Lab, Boston, 2023) - , , , , :
The Design Process for Monolithically Manufactured Millimeter-Wave Antenna Arrays Using Stereolithography 3D Printing.
IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (San Diego, 2023). DOI: 10.1109/IMS37964.2023.10188155 - , , , , , :
Accurate Heart Beat Detection with Doppler Radar using Bidirectional GRU Network.
IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium (Las Vegas, 2023). DOI: 10.1109/RWS55624.2023.10046202 - , , , , , :
Contactless In-Bed Movement in Various Scales Classification with CW Radar.
20th European Radar Conference, EuRAD 2023 (Berlin, 2023). DOI: 10.23919/EuRAD58043.2023.10289241 - , , , , , , :
Palliative Care and new technologies. The use of smart sensor technologies and its impact on the Total Care principle.
BMC Palliative Care (2023). ISSN: 1472-684X. DOI: 10.1186/s12904-023-01174-9 - , , , , :
Catch Your Breath!: Vital Sensing for Radar.
IEEE Microwave Magazine 24 (2023), S. 75-82. ISSN: 1527-3342. DOI: 10.1109/MMM.2022.3226546 - , , , , :
Heart Sound Detection Using an Ultra-Wideband FMCW Radar.
IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (San Diego, 2023). DOI: 10.1109/IMS37964.2023.10188202 - , , , , , , , , , :
Influence of Sensor Position and Body Movements on Radar-Based Heart Rate Monitoring.
IEEE-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI) (Ioannina, 2022). DOI: 10.1109/BHI56158.2022.9926775. URL: https://www.mad.tf.fau.de/files/2022/11/herzer_muecke22_validation_mis.pdf - , , , , , , , , :
A Lightweight Robust Approach for Automatic Heart Murmurs and Clinical Outcomes Classification from Phonocardiogram Recordings.
Computing in Cardiology (CinC) (Tampere, 2022). DOI: 10.22489/CinC.2022.165





